Table of Contents
ToggleImagine a world where machines not only talk to each other but also make your morning coffee, well, they might be getting closer. Welcome to the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), a transformative force revolutionizing industries everywhere. From manufacturing to energy, IIoT is orchestrating operations like a skilled conductor leading a symphony. This article will take you on an engaging journey through the nuts and bolts of IIoT, its applications, and even some challenges that might trip it up along the way. So grab your hard hat and let’s jump into the extraordinary world of IIoT.
Understanding The Industrial Internet Of Things

At its core, the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) refers to the integration of internet connectivity in industrial devices and machinery. This connectivity enables data exchange and communication between devices, creating a smart ecosystem designed to optimize operations, enhance productivity, and reduce costs.
Key Components Of IIoT
The landscape of IIoT is built upon several key components:
- Sensors: Devices that collect valuable data from the environment. Sensors detect variables such as temperature, pressure, and humidity, providing crucial information that can drive decision-making.
- Connectivity: The backbone of IIoT. This involves numerous network technologies, from Wi-Fi to cellular and LPWAN (Low Power Wide Area Network), facilitating data exchange without human intervention.
- Data Management Platforms: These platforms analyze and store the data collected from various sensors. They help businesses make sense of the mass of information, turning raw data into actionable insights.
- Machine Learning and AI: Advanced algorithms work tirelessly behind the scenes to learn from historical data and enhance predictive maintenance, allowing businesses to anticipate failures before they disrupt operations.
- User Interface: A dashboard or interface that allows users to visualize and control IIoT systems in real-time. This is where the magic happens, bringing insights to life and facilitating quick decision-making.
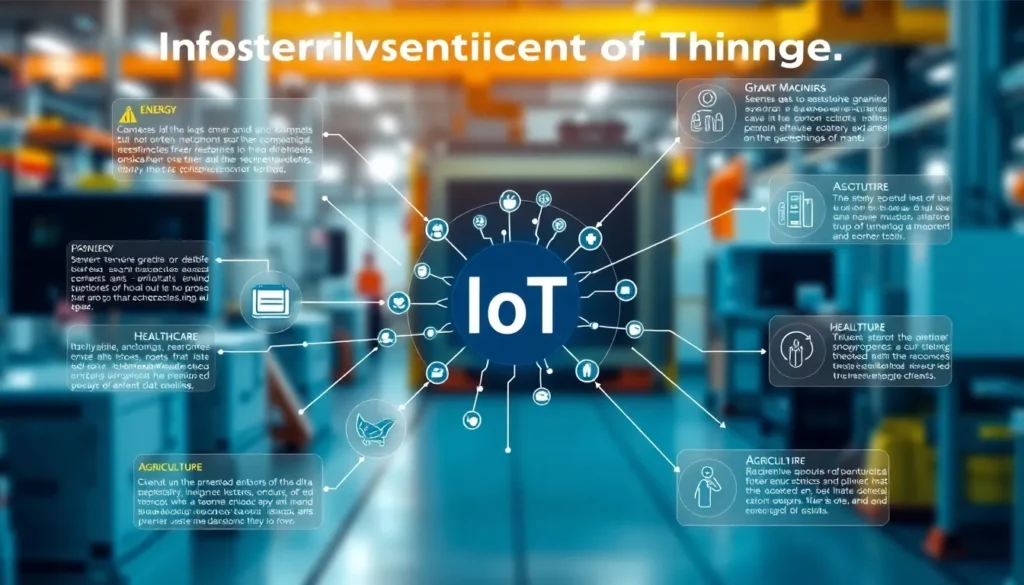
Applications Of IIoT Across Industries
The applications of IIoT are as diverse as its components. Here are a few ways that various sectors harness its power:
- Manufacturing: Smart factories leverage IIoT to monitor machinery performance and predict failures, reducing downtime and optimizing production processes. Using real-time analytics can significantly streamline operations.
- Energy: In the energy sector, IIoT enables better monitoring of resources, such as gas and electricity. Smart grids enhance efficiency by balancing supply and demand, ensuring that energy consumption is optimized.
- Healthcare: IIoT can revolutionize patient care by enabling remote monitoring of health data through wearable devices. This leads to timely interventions and improved patient outcomes.
- Transportation: Fleet management systems use IIoT for route optimization, real-time tracking, and predictive maintenance, eventually reducing operational costs.
- Agriculture: Precision farming techniques use IIoT for soil monitoring and crop health assessment, leading to higher yields and more efficient resource use.
Challenges In Implementing IIoT Solutions
Even though its many advantages, implementing IIoT solutions comes with its fair share of hurdles. Understanding these challenges can better prepare organizations to navigate them effectively:
- Data Security: The risk of cyberattacks is heightened as more devices connect to the internet. Ensuring robust security measures is imperative to protect sensitive data.
- Interoperability: Compatibility issues often crop up when integrating new IIoT devices with existing infrastructure. Different protocols can create inconsistencies, which makes smooth communication difficult.
- Scalability: As businesses grow, scaling IIoT solutions can become complex. Organizations must ensure that their underlying architecture can adapt to increasing data volume and device connectivity.
- Data Management: The sheer volume of data generated can overwhelm existing analytics systems. Companies need strategic plans for data management to extract meaningful insights efficiently.
Best Practices For IIoT Implementation
For successful IIoT implementation, several best practices come into play that organizations should adhere to:
- Define Clear Objectives: Establish clear goals for what the IIoT implementation aims to achieve. Whether it’s reducing downtime or improving supply chain visibility, clarity is key.
- Invest in Scalable Infrastructure: Using a cloud-based infrastructure can provide the flexibility and scalability needed as IoT demands increase over time.
- Ensure Robust Security Measures: Carry out multi-layered security strategies that protect end devices, networks, and data. Regular audits and updates are necessary to counter emerging threats.
- Train Staff: Continuous training ensures that employees can navigate IIoT systems. They need to be equipped with the skills to interpret data and make informed decisions.
The Future Of IIoT: Trends And Predictions
As technology continues to evolve, so will the Industrial Internet of Things. Here are some anticipated trends:
- Enhanced AI and Machine Learning Integration: Expect more advanced algorithms capable of predicting failures and optimizing resource management on an unprecedented scale.
- Increased Focus on Sustainability: As industries seek greener practices, IIoT can help monitor resource consumption and minimize waste, contributing to sustainable operations.
- 5G Connectivity: The advent of 5G will help faster and more reliable internet connections, enabling real-time analytics and even more efficient communication among devices.
- Collaborative Robots (Cobots): The rise of cobots working alongside human operators is on the horizon, promoting efficiency without compromising safety.